Non-Psychoactive Edibles
If you eat raw weed not much will happen. This is because the THCa has yet to be decarboxylated into the psychoactive THC that can be metabolized readily by the body. Some popular non-psychoactive edibles include juices, flour, or salads.
Raw cannabis is a great source of complete protein and is loaded with vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids.
Psychoactive Edibles

If you eat weed that has been decarboxylated, they will be 5x more psychoactive than when you smoke cannabis. Because cannabinoids are hydrophobic and are fat- soluble you can extract THC into any fat or alcohol.
Effects of Eating Psychoactive Edibles
The effects of eating psychoactive edibles will vary from strain to strain, depending on its cannabinoid and terpene profile. Generally, you can expect the following effects:
Psychoactive edibles are categorized by the way cannabinoids are absorbed into your system and can be in one or both of these categories.
Gastrointestinal EdiblesCannabinoids are absorbed into the body through G.I. tract and liver. Examples include:
| Sublingual EdiblesCannabinoids are absorbed through the mucous membrane in your mouth, especially under your tongue. Examples include:
|
Endocannabinoid System

Cannabinoid receptors are located throughout the body and are part of the endocannabinoid system. This system is involved in regulating many physiological processes including appetite, pain-sensation, mood, and memory.
As cannabis is digested, cannabinoids enter the bloodstream. After the cannabinoids cross the blood brain barrier where they lock into C1 and C2 cannabinoid receptors. The cannabinoids interact with the brain and indirectly increase dopamine by blocking the action of another neurotransmitter called GABA.
Cannabinoids
The majority of the effects of an edible depend on the cannabinoids. With over 400 cannabinoids present in cannabis we don’t know how all of them work yet. THC, CBD, and CBN are the most abundant cannabinoids followed by CBC, CBG, and THCV.
The mixture of cannabinoids produced by a plant is known as the plant’s ‘cannabinoid profile’. Selective breeding has been used to control the genetics of plants and modify the cannabinoid profile.
Strains that are used as hemp fiber are bred so they are low in psychoactive chemicals like THC. Strains used in medicine are often bred for high CBD content, and strains used for recreational purposes are usually bred for high THC content or for a specific mixture of cannabinoids.
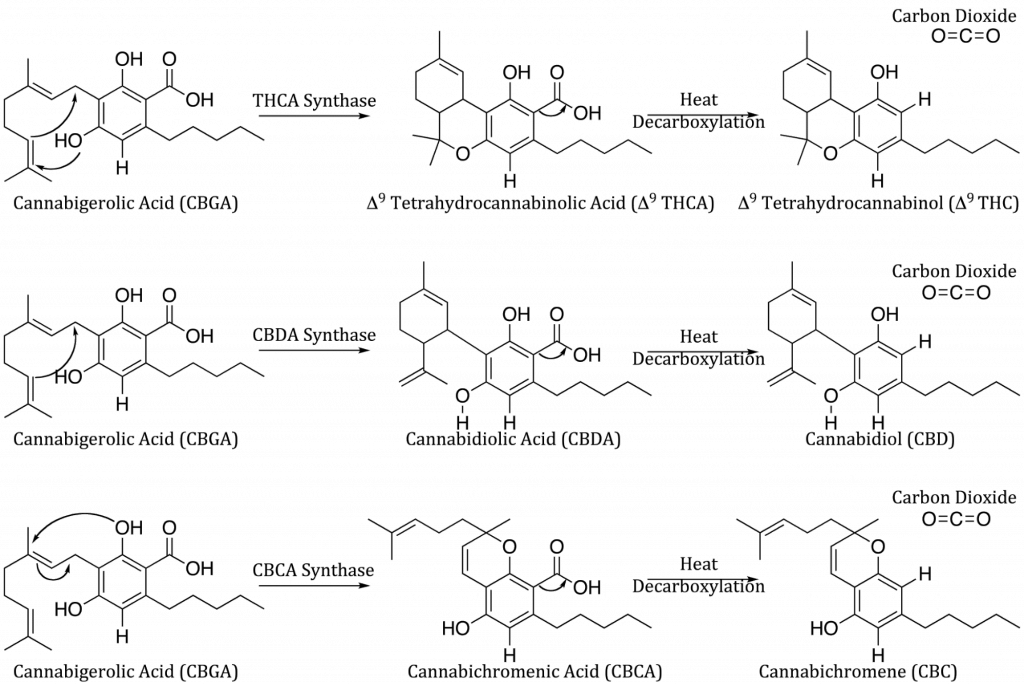
The Life of Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids change throughout their existence and so do their effects. CBGA or Cannabigerolic Acid is the building block of the major psychoactive components in cannabis. Depending on which synthase enzyme the CBGA comes into contact with will determine which cannabinoid it will turn into.
Next, through the decarboxylation process, a carboxyl group is released and creates the final cannabinoid forms we can absorb such as THC, CBD, and CBC.
THC – Tetrahydrocannabinol314.6F Vaporization Temperature
| Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the primary psychoactive compound in Cannabis. When processed by your liver, delta-9 THC is converted to 11-hydroxy THC, which is up to 5x as psychoactive. Physical EffectsHelps in alleviating migraines, pain, stress, depression, PTSD epilepsy, asthma, inflammation. Helps increase appetite. Mental EffectsHappy, social, relaxed. euphoria, well-being, relaxation or stress reduction, increased appreciation of the arts, including humor and music, joviality, introspection, increased sensuality, increased awareness of sensation, increased libido, and creativity.
|
THCV – Tetrahydrocannabivarin428F Vaporization Temperature
| Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV) is prevalent in sativa strains. It’s an antagonist of THC at CB1 receptors and emulates THC’s psychoactive effects.Physical EffectsAppetite suppression, energetic, alert. Mental EffectsHappy, social, motivated euphoria. |
CBG – Cannabigerol125.6F Vaporization Temperature
| CBG is non-psychoactive and is the precursor to other Cannabinoids. CBG is low in concentration in most strains.Physical EffectsMigraine relief anti-inflammatory and antioxidant analgesic, anti-bacterial, reduces intraocular pressure has been shown to inhibit tumor growth in mice. Mental EffectsNon-psychoactive in itself but is believed to balance the anxiety and paranoia that THC can produce, creating a more relaxed high. |
CBC – Cannabichromene428F Vaporization Temperature
| Cannabichromene (CBC) is non-psychoactive. CBC has shown antitumor effects in breast cancer samples in mice. It’s more commonly found in tropical cannabis varieties.Physical EffectsAnti-inflammatory, antibiotic, antifungal, CBC helps promote neurogenesis, anti-diarrheal Mental EffectsHappy, antidepressant effects when combined with THC/CBD. |
CBD – Cannabidiol320-356F Vaporization Temperature
| Cannabidiol (CBD) is non-psychotropic. Cannabidiol has trouble binding to the CB1 and CB2 receptors. Instead, it helps the effects of other cannabinoids however, it does counteract the cognitive impairment associated with THC. CBD has also been shown to play a role in preventing the short-term memory loss associated with THC.Physical EffectsHelps stop seizures caused by epilepsy and alleviates migraines, pain, anxiety, depression and make you feel happy, social, and relaxed as a synergist to THC. Reduces nausea and vomiting, combats inflammatory disorders. Mental EffectsCalm, social, relaxed, couch lock also combats psychosis disorders of the mind. |
CBN – Cannabinol365F Vaporization Temperature
| Cannabinol (CBN) is the primary product of THC when it breaks down and there is usually little of it in a fresh plant. CBN content increases as THC degrades in storage because of exposure to light and air. Its binds more readily to the CB2 receptor than to the CB1 receptor but are only mildly psychoactive.Physical EffectsPain relief, anti-insomnia, promotes the growth of bone cells, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, anti-convulsive, appetite stimulant. Mental EffectsGrogginess, dizziness, confusion, sleepy. |
Terpenes
Terpenes account for the majority of the taste and smell of cannabis. Terpenes are present in the plant’s resin glands, known as kief or trichomes. Terpenes are not only found in cannabis but are also in 100’s of other plants and are typically associated with smell and taste of pepper, pine needles, and citrus fruits.
With over 140 terpenes available in thousands of combinations in different strains, you have the ability to choose the one that pairs perfectly with any food if you understand these different terpenes. The following five will give you a good understanding of the most well known and sought after flavors.
Pinene

Found in pine needles, rosemary, basil, parsley, and dill. Pinene has a piney, volatile scent and flavor profile.
Alpha-pinene is a bronchodilator, antibiotic and has anti-inflammatory properties. It also seems to enhance memory.
Linalool

Linalool has a sweet, floral, woody and lavender-like scent and is found mainly in flowers and spices such as lavender, mint, cinnamon, and rosewood.
Linalool is anti-anxiety, anticonvulsant, antidepressant, and anti-acne.
Myrcene

Myrcene has a slightly bitter herby taste characteristic. Myrcene is found in hops, thyme, bay, and parsley.
Myrcene acts as an analgesic, muscle relaxant, and may have antibiotic properties.
Beta-caryophyllene

Found in black pepper, this terpene contributes a spicy peppery flavor profile.
It tends to have anti-anxiety, antidepressant, antioxidant, and antimicrobial effects
Limonene

As the name of this terpene suggests, limonene has a citrus taste. Found in fruit rinds, rosemary, and peppermint.
Improves mood, anti-anxiety, antidepressant, immune booster. Limonene’s tastes great in many dishes, especially drinks and desserts.
Flavor Pairing
Just like any other food, there are certain flavors that pair well together. Using the following chart you can choose the perfect wine and strain to go with your dish. Keep in mind that growing conditions change the level of terpenes found in a strain and the only way to tell how much is in a strain is to get it tested.
| Pinene | Linalool | Myrcene | Caryophyllene | Limonene |
| found in | ||||
| – Jack Herer – Chemdawg – Trainwreck | – G-13 – Amnesia Haze – Lavender – LA Confidential | – Pure Kush – Himalayan Gold – Skunk #1 – White Widow | – Hash Plant – OG Kush – Bubba Kush – Chemdawg | – OG Kush – Super Lemon Haze – Jack the Ripper – Lemon Skunk |
| tastes good in | ||||
| – Lasagna | – Hard Candies – Brownies | – Mango salsa | – Steak | – Cheesecake – Lemon Bars |
| with a glass of | ||||
| – Pinotage – Malbec | – Sherry – Grenache Rose | – Chardonnay -White Merlot | – Pinot Noir – Merlot | – Moscato – Pinot Grigio |
Synergistic Effects
The effects of cannabis are known to be different when cannabinoids are consumed alone versus combined, this is known as the synergistic or entourage effect. Research shows that these synergistic effects can lead to 3-4x greater medical efficacy.
THC | |||||
| synergizes with | |||||
| CBD | CBN | alpha-pinene | beta caryophyllene | limonene | myrcene |
| to be | |||||
| antidepressant antiepileptic | antiepileptic | antiasthma | antidepressant | antiasthma antidepressant | relaxes muscles couch-lock
|
CBD | |||||
| synergizes with | |||||
| CBD | CBN | alpha-pinene | beta caryophyllene | limonene | myrcene |
| to be | |||||
| antidepressant antiepileptic | antiepileptic | antiasthma | antidepressant | antiasthma antidepressant | anti inflammatory anti-cancer
|
CBN | |||||
synergizes with | |||||
| CBD | CBN | alpha-pinene | beta caryophyllene | limonene | myrcene |
| to be | |||||
| antidepressant antiepileptic | antiepileptic | antiasthma | antidepressant | antiasthma antidepressant | anti-cancer |